In this ever-evolving world of technology, website has become the most common and important touchpoint for any business. With the unpredictable and rapid technological advancements, the adaptability of a business’s website becomes a critical factor for its growth.
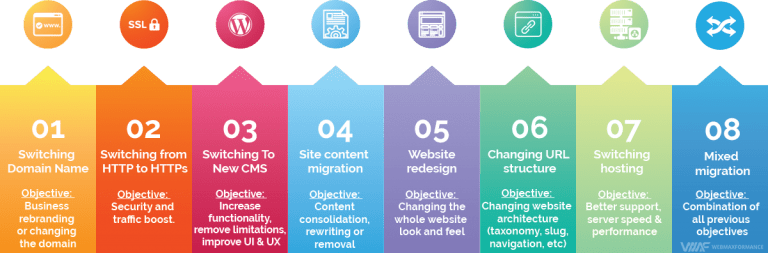
Site Migration is a way of adapting to the changes, which refers to the substantial alterations within the website which are generally carried out to update its platform, protocol (http to https), structure, domain/subdomain or UI/UX. Some of the most common situations for executing website migration are as follows:
- Domain name change – Rebranding of business or movement from one domain to another
- Subdomain change – Migration between folders or subdirectories
- Re-platforming – When the website’s platform is being changed, like Shopify to WordPress
- Protocol change – Migration from HTTP to HTTPS
- Redesign – Modifications involving complete site revamp or major code-level changes
- Top-level domain name change – Usually when an international business wants the website to migrate to or from country code top level domain
- Site Structure change – Alteration in the architecture/taxonomy of the website
Migration not only enables the business to achieve a better functionality, but also provides an opportunity to investigate and rectify the existing errors. However, these changes can have a consequential impact on the website’s visibility in the Organic Search if not executed mindfully. Bad migration can result in loss of organic traffic and revenue because a poorly migrated website gives out negative signals to the search engine spiders, which results in reduced visibility on the search engine’s result pages.
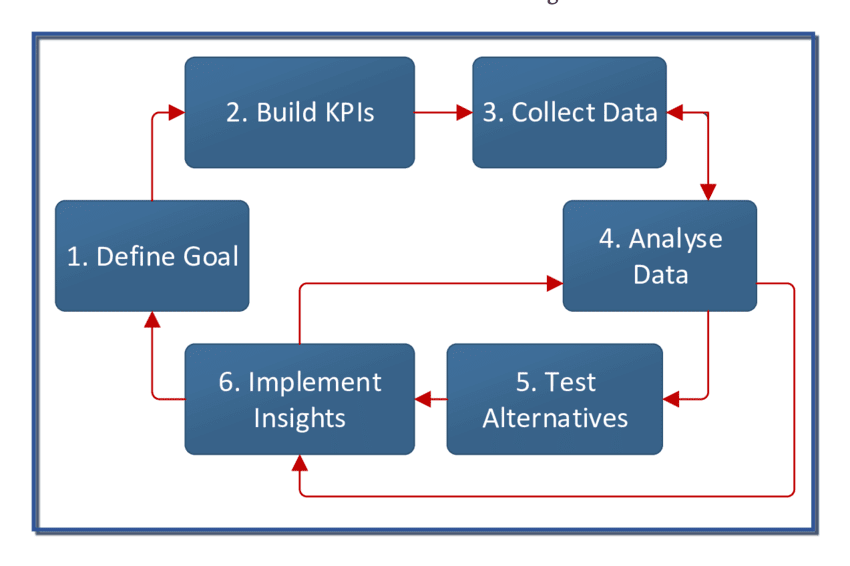
Since migration can make or break a website, it is extremely important to follow the best practices in order to ensure a technologically robust and SEO-compliant website. The process consists of 3 broad phases, i.e. before, during and after migration, with a list of important checkpoints that should be followed to ensure that the new website positively achieves the goal behind migration while retaining the SEO value of the legacy website.
Pre-Migration
Pre-migration phase incorporates benchmarking performance of the legacy website and ensuring that the elements important from an SEO standpoint are retained in the revamped version.
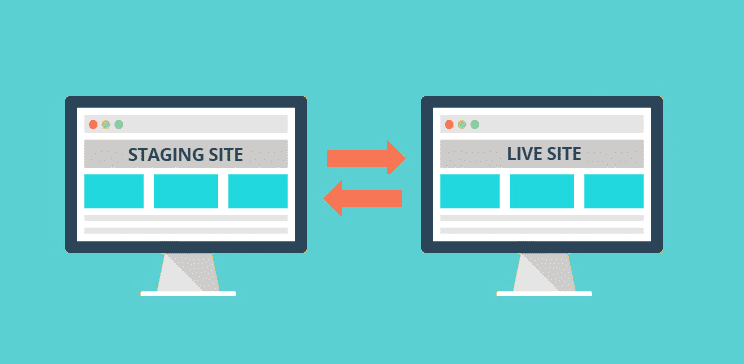
Staging Server
Ensure that the staging server is not be accessible by the search engines but can be crawled by search engine spiders on demand. This will help with A/B testing and checking if there are any crawlability issues with any element present on a typical webpage. The staging server should also be crawled to check for any broken links, incorrect tags, duplication and 404 pages.
Page Template
Review the page template to ensure that the following essential SEO elements are in place:
- Page
Title - Meta
Tags - Canonical
Tags - Header
Tags - Image
Alt Attributes - Body
Content
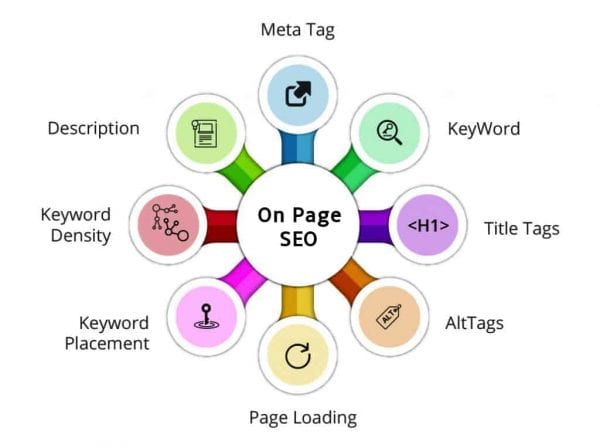
Depending on the type of migration scheduled, the features mentioned above are most likely to get affected. These elements are the building blocks of a successful SEO project and any unintentional change should be treated on priority. The page template of the new website should also be tested to check for any JavaScript crawling issues. Crawlability issue with any of the elements mentioned above can deteriorate the ranking of a webpage on Organic Search.
Custom 404 Page
Migration of a website might give rise to an increased number of unavailable or 404 pages. This results in a bad user experience and reflects in the form of higher bounce rates. In order to encourage the consumer to check out other functional sections of the website, it must have a custom 404 page with links to all the useful parts of the website like:
- Homepage
- Top
Navigation Bar - HTML
Sitemap (directory) - Internal
Site Search
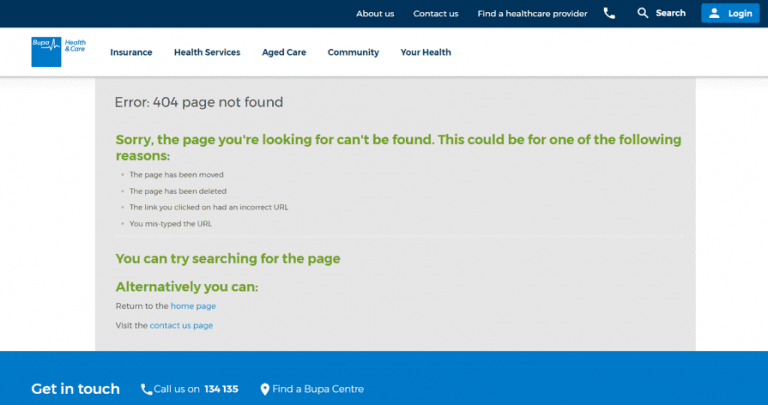
This is a fail-safe measure deployed to aid user engagement, during and post migration.
Page Speed Analysis
Page speed is considered as one of the major ranking factors by Search Engines because the loading speed of various elements of a webpage directly impact the user experience. Page speed analysis of the legacy website must be carried out for performance benchmarking, especially for migrations involving platform switch or code-level redesign. Webtools like GTmetrix and Google’s Lighthouse provide an in-depth analysis of the load times for various elements in a page and the possible solutions for further optimization.
Analytics
Tracking website activity using Google Analytics, Adobe Omniture or any reliable analytical tool provides holistic insights about the business. Hence, recording information like number of sessions, conversions, revenue, bounce rate, landing pages, channel attribution, etc. is a must for analyzing any website. Ensuring that the new website has analytics set-up correctly with defined event tracking, shall enable the business to assess and compare historic performance of the website.
Benchmark Performance
To assess the impact of migration, the following key performance indicators of the legacy website must be recorded:
- keyword
position/ranking - number
of indexed pages - number
of sessions - lead/conversions
- average
bounce rate - number
of 404 pages
Duplicate Content
Migration provides an opportunity to identify and fix any error present in the legacy website. Presence of duplicate content on the website eventually affects its position on Organic Search, as it confuses the search engine spiders. Identifying duplication issues and fixing them using appropriate methods like 301-redirection or inclusion of canonical tags will spare the website from getting penalized and optimize the crawl budget in the process.

Taxonomy
The site’s hierarchy and URL structure are extremely important from an SEO standpoint. An optimized taxonomy helps the SEO juice to pass on to the inner-most pages of the website efficiently. The URL of a webpage is another opportunity for introducing keywords and a carefully defined URL structure should enable the webpage to gain substantial authority on Organic Search.
Redirection Module
Before commencing migration, a list of all the important pages of the legacy website should be extracted and mapped to their corresponding URLs of the new website. A 301-redirection module should be setup to map the URLs in order to ensure that all the SEO authority garnered by the legacy website is passed on its newer counterpart. It also helps the search engine spiders understand that a website migration has taken place.
Image Source: The too many redirects issue: How to fix it
Sitemap
Sitemap consists of a list of all the important URLs of a website. It ensures that all the significant pages of a website are visible and accessible to the search engine spiders as well as the user. After setting up the redirection module, generate an XML and HTML sitemap for the new website. The XML sitemap is perceived as a directory by search engine spiders, while the HTML sitemap serves as a directory for the user. A link to the HTML sitemap should be included in the custom 404 page of the new website for aiding the user’s engagement.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt file holds information pertaining to the accessibility of the website for the search engine spiders and similar agents. The last step, prior to migration, should involve generation of a robots.txt file which contains directives that aim at optimizing crawl budget. The XML sitemap’s URL should also be included in the robots.txt file to ensure that all the important pages of the website are available for crawling.
Image Source: Robots Checker
During Migration
It is critical to execute migration in phases to ensure the complete website does not take a hit in the process. To minimize the negative effects, the activity can ideally be divided into two phases, namely analytical-technical assessment and content assessment. The least important pages from the business’s perspective must be taken up for migration first. This phase enables to check for any technical faults in the framework and structure of the webpage. After the technical evaluation, the revamped set of webpages are assessed for their content retention vis-à-vis their legacy counterparts.
The following checks need to be performed during migration phase to ensure a technically sound and SEO friendly website:
Analytics
Ensuring that every analytical aspect of the webpage is being tracked for performance will enable the efficient execution of the forthcoming processes involved in the activity. The performance parameters of the revamped pages should be compared with their historic data to gauge the extent of any negative impact on the website. The migration should be annotated within the reporting platform for future reference.
404 Pages
Generation of 404 or soft-404 pages is very common when executing re-platforming and redesign. The HTTP status of the revamped pages need to be monitored to detect any occurrence of a “dead-end” page.
Redirection
It is important to reinforce the redirection module (in case of URL change) for the revamped pages to safeguard the SEO authority of legacy website. While migrating, every important page from the legacy website should be redirected to the new URL using one and only one 301-permanent redirect. A chain of redirections is treated as a negative signal by the search engine spiders, which can hamper the performance of concerned pages on Organic Search.
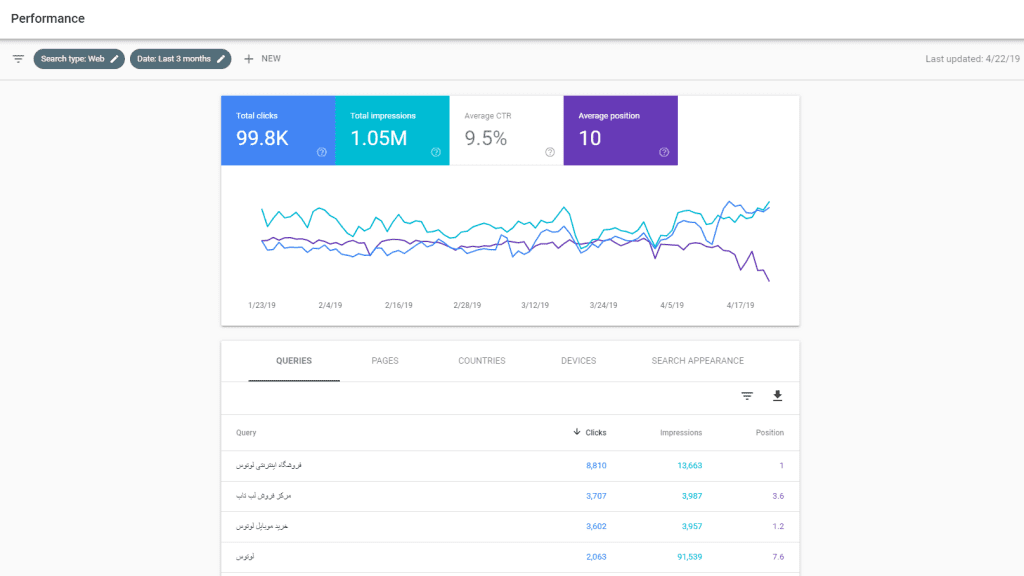
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an excellent tool to assess the health of a website. Submitting the change of domain address (if any), revised robots.txt file and a link to the altered XML sitemap will help monitor the effects of migration post the activity.
Post-Migration
Congratulations on your new and improved website! The phase after successful migration of the website involves conducting performance-oriented checks using the benchmarked data. It also incorporates executing optimization activities to build up the SEO authority for the revamped version.
The following tasks serve as the finishing touches for a accomplishing a successful migration:
Technical Audit
A complete technical audit needs to be carried out as a final assessment for framework and structure of the renovated website. Some of the crucial factors to check are as follows:
- Site architecture and navigation
- Indexation and duplication issues
- Missing or duplicate on-page content
- Crawling errors and status code check
- Page load speed
- Mobile usability
- Structured markup check
- SEO-friendly pagination
- Sitemap issues
Google Search Console
The GSC needs to be monitored daily to check for any hiccups related to the refurbished website. The important pages of the website which have not yet been discovered by the search engine spiders, need to be submitted individually to Google’s Search Console for fetching and rendering across devices.
Reporting Platforms
The after-effects of migration can be easily summarized by closely monitoring the following information from reporting platforms:
- Total number of pages indexed
- Submitted vs. Indexed pages (via XML sitemap)
- Pages receiving at least 1 organic visit
- Number of “not found” pages
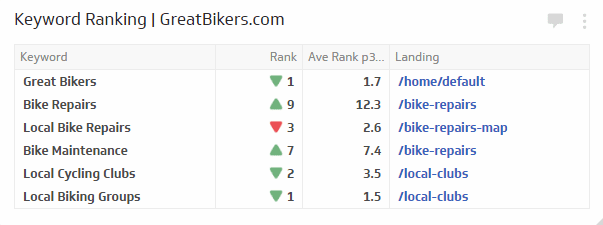
Keyword Performance
Keyword performance or rankings reflect the historic SEO efforts combined with the fruitfulness of website migration. The keywords can ideally be segregated into the following buckets for monitoring and comparing performance on Organic Search:
- Brand
and non-brand terms - Seasonal
and non-seasonal terms - Across
devices (mobile and desktop)
Google My Business
The GMB profile of the business should be updated with the new domain/business details and social profile. This will aid the local customer engagement across Google Search and Maps.
Image Source: How to optimize Google My Business listings for multi-location businesses
Backlinks
A typical website is bound to lose SEO authority post migration. This impact can be minimised by building fresh, authoritative links to the new domain. Obtaining links from reliable and authentic websites will help improve the performance of the website on Organic Search.
To Conclude
Website migration can be tricky but if executed mindfully, it can tremendously boost a business’s visibility on Organic Search. We hope that this blog serves as an SEO checklist for executing website migration and helps you achieve a technologically robust and SEO-friendly website. If you are a website owner looking to migrate to a new domain, technology, framework or design, contact the experts at SEO London now!